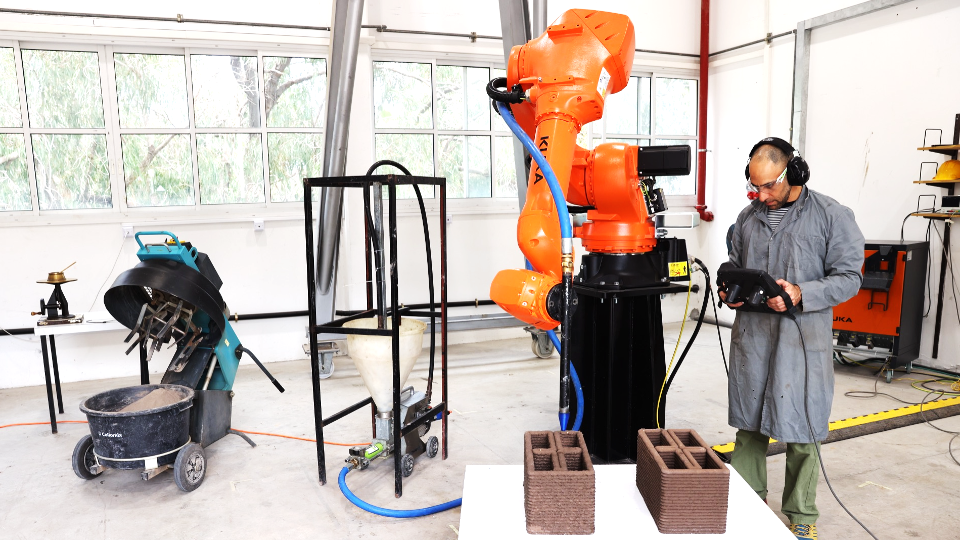

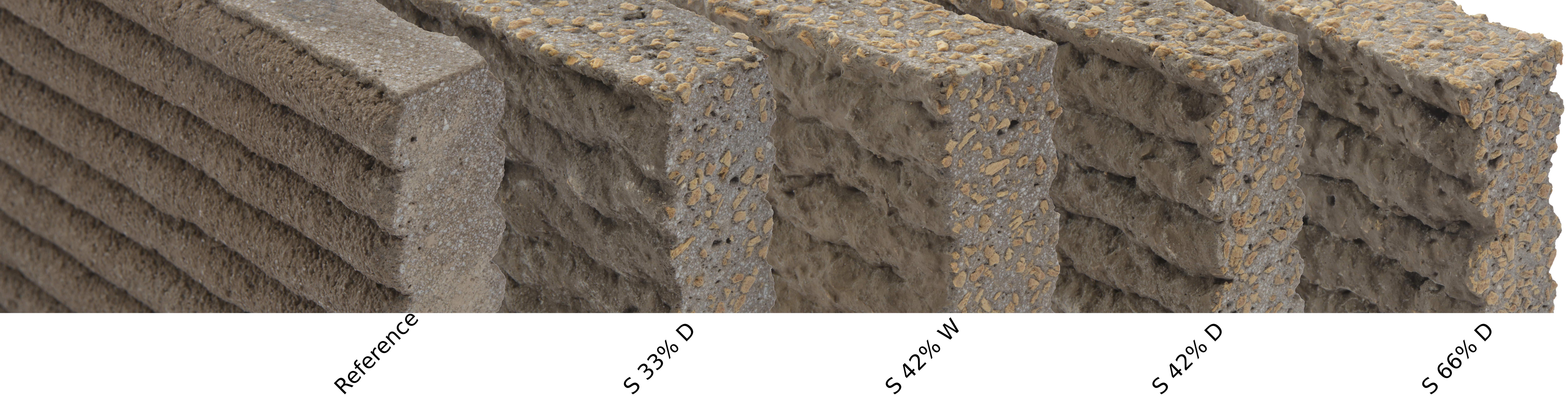
This study explores the potential of cork-cement composites for structural and thermal performance in architecture through additive manufacturing (AM) technology. By optimizing the composite for 3D printing, the research demonstrates the unique applicability of this composite for large-scale architectural projects, particularly for building envelope elements. Employing a robotic 3D printing process, masonry blocks were manufactured and evaluated for structural performance and thermal efficiency. The results of this study demonstrate the practicality of using cement-cork composite in AM architectural envelopes. In addition, the results show that 3D-printed cork-cement composite elements outperform traditional masonry blocks. Ultimately, this study paves the way for future 3D printing of architectural elements with functionally graded structural and thermal performance.
Ohad Yaacov Meyuhas
Pavel Larianovsky
Jonathan Natanian
Aaron Sprecher